药品详细
Cimetidine(西咪替丁)
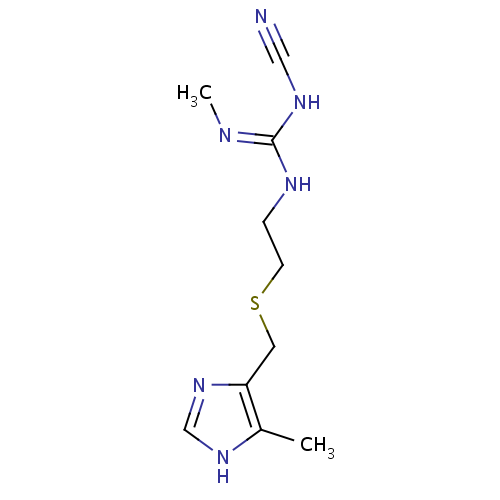
化学结构式图
中文名
西咪替丁
英文名
Cimetidine
分子式
C10H16N6S
化学名
(Z)-1-cyano-2-methyl-3-(2-{[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}ethyl)guanidine
分子量
Average: 252.339
Monoisotopic: 252.115715232
Monoisotopic: 252.115715232
CAS号
51481-61-9
ATC分类
A02B 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
Acibilin;Acinil;Cimal;Cimetag;Cimetum;Dyspamet;Edalene;Eureceptor;Gastromet;Peptol;Tagamet;Tagamet HB;Tagamet HB 200;Tametin;Tratul;Ulcedin;Ulcedine;Ulcerfen;Ulcimet;Ulcofalk;Ulcomedina;Ulcomet;Ulhys;
同义名
Cimetidine A/AB;Cimetidine Hcl;
基本介绍
A histamine congener, it competitively inhibits histamine binding to histamine H2 receptors. Cimetidine has a range of pharmacological actions. It inhibits gastric acid secretion, as well as pepsin and gastrins output. It also blocks the activity of cytochrome P-450 which might explain proposals for use in neoadjuvant therapy. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Actavis mid atlantic llc
- Apotex inc
- Contract pharmacal corp
- Dava pharmaceuticals inc
- Duramed pharmaceuticals inc sub barr laboratories inc
- Endo pharmaceuticals inc
- Glaxosmithkline
- Hi tech pharmacal co inc
- Hospira inc
- Ivax pharmaceuticals inc sub teva pharmaceuticals usa
- L perrigo co
- Lek pharmaceuticals d d
- Luitpold pharmaceuticals inc
- Mylan pharmaceuticals inc
- Novex pharma
- Perrigo co
- Pharmaceutical assoc inc div beach products
- Pliva inc
- Roxane laboratories inc
- Sandoz inc
- Teva parenteral medicines inc
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa inc
- Watson laboratories inc
- Wockhardt eu operations (swiss) ag
封装厂家
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Services Inc.
- Amerisource Health Services Corp.
- Amneal Pharmaceuticals
- Apotex Inc.
- Apotheca Inc.
- A-S Medication Solutions LLC
- Baxter International Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.
- Bryant Ranch Prepack
- Cardinal Health
- Central Texas Community Health Centers
- Comprehensive Consultant Services Inc.
- Darby Dental Supply Co. Inc.
- DAVA Pharmaceuticals
- Direct Dispensing Inc.
- Dispensing Solutions
- Diversified Healthcare Services Inc.
- Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- GlaxoSmithKline Inc.
- Group Health Cooperative
- H.J. Harkins Co. Inc.
- Heartland Repack Services LLC
- Hi Tech Pharmacal Co. Inc.
- Hospira Inc.
- Ivax Pharmaceuticals
- Kaiser Foundation Hospital
- Keltman Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Lake Erie Medical and Surgical Supply
- Lek Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Liberty Pharmaceuticals
- Major Pharmaceuticals
- Medisca Inc.
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
- Mylan
- Novex Pharma
- Novopharm Ltd.
- Nucare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Palmetto Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- PCA LLC
- PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Perrigo Co.
- Pharma Pac LLC
- Pharmaceutical Association
- Pharmedix
- Pharmpak Inc.
- Physicians Total Care Inc.
- Pliva Inc.
- Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Prepackage Specialists
- Prepak Systems Inc.
- Prescription Dispensing Service Inc.
- Qualitest
- Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Sandhills Packaging Inc.
- Sanofi-Aventis Inc.
- Southwood Pharmaceuticals
- St Mary's Medical Park Pharmacy
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Torpharm Inc.
- Tya Pharmaceuticals
- UDL Laboratories
- United Research Laboratories Inc.
- Va Cmop Dallas
- Wockhardt Ltd.
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
gastric acid RELATED DISORDERS 中和胃酸;
药理
| Indication | For the treatment and the management of acid-reflux disorders (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, heartburn, and acid indigestion. | ||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Cimetidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist. It reduces basal and nocturnal gastric acid secretion and a reduction in gastric volume, acidity, and amount of gastric acid released in response to stimuli including food, caffeine, insulin, betazole, or pentagastrin. It is used to treat gastrointestinal disorders such as gastric or duodenal ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and pathological hypersecretory conditions. Cimetidine inhibits many of the isoenzymes of the hepatic CYP450 enzyme system. Other actions of Cimetidine include an increase in gastric bacterial flora such as nitrate-reducing organisms. | ||||||
| Mechanism of action | Cimetidine binds to an H2-receptor located on the basolateral membrane of the gastric parietal cell, blocking histamine effects. This competitive inhibition results in reduced gastric acid secretion and a reduction in gastric volume and acidity. | ||||||
| Absorption | Rapid 60-70% | ||||||
| Volume of distribution | Not Available | ||||||
| Protein binding | 15-20% | ||||||
| Metabolism |
Hepatic
|
||||||
| Route of elimination | The principal route of excretion of cimetidine is the urine. | ||||||
| Half life | 2 hours | ||||||
| Clearance | Not Available | ||||||
| Toxicity | Symptoms of overdose include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, increased saliva production, difficulty breathing, and a fast heartbeat. | ||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||
| Pathways |
|
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Acenocoumarol | Cimetidine may increase the anticoagulant effect of acenocoumarol. |
| Alfentanil | Increases the effect of the narcotic |
| Alprazolam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, alprazolam. |
| Aminophylline | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of aminophylline by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of aminophylline if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Amitriptyline | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, amitriptyline, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of amitriptyline if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Amoxapine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, amoxapine, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of amoxapine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Anisindione | Cimetidine may increase the anticoagulant effect of anisindione. |
| Astemizole | Increased risk of cardiotoxicity and arrhythmias |
| Atazanavir | This gastric pH modifier decreases the levels/effects of atazanavir |
| Bendamustine | CA1A2 hepatic enzyme metabolism is affected by increased amounts of bendamustine by cimetidine. In addition, decreased conversion of bendamustine to active metabolites occurs. Amounts of active metabolites may be decreased. Decreased conversion of bendamustine to active metabolites also occurs. |
| Bromazepam | Co-administration with cimetidine will cause a reduction in bromazepam clearance and increases half-life. |
| Carbamazepine | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of carbamazepine during the first few days of concomitant therapy. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of carbamazepine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Carmustine | Increases myelosuppression caused by carmustine |
| Cefditoren | H2-Antagonists such as cimetidine may decrease the serum concentration of cefditoren. Cefditoren prescribing information recommends to avoid concomitant use with H2-antagonists (eg, famotidine, ranitidine) and antacids as well. Consider alternative methods to minimize/control acid reflux (eg, diet modification) or alternative antimicrobial therapy if use of H2-antagonists can not be avoided. |
| Chlordiazepoxide | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide. |
| Clomipramine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, clomipramine, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of clomipramine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Clonazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, clonazepam. |
| Clorazepate | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, clorazepate. |
| Clozapine | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentratin of clozapine. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of clozapine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Codeine | Cimetidine may decrease the therapeutic effect of codeine by decreasing its metabolism to its active metabolite, morphine. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic effect of codeine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Desipramine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, desipramine, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of desipramine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Diazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, diazepam. |
| Dicumarol | Cimetidine may increase the anticoagulant effect of dicumarol. |
| Dihydroquinidine barbiturate | Increases the effect of quinidine |
| Dofetilide | Increases effect/toxicity of dofetilide |
| Donepezil | Possible antagonism of action |
| Doxepin | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, doxepin, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of doxepin if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Dyphylline | Increases the effect of theophylline |
| Eltrombopag | Affects hepatic CYP1A2 metabolism, will decrease effect/level of eltrombopag. Affects hepatic CYP2C9/10 metabolism, will decrease effect/level of eltrombopag. |
| Enoxacin | Cimetidine may decrease the absorption of enoxacin. |
| Epirubicin | Cimetidine can increase epirubicin levels |
| Estazolam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, estazolam. |
| Ethotoin | Increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Fentanyl | Cimetidine, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, may decrease the metabolism of fentanyl. Closely monitor changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of fentanyl if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Flecainide | Cimetidine, a moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor, may decrease the metabolism of flecainide. |
| Flurazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, flurazepam. |
| Fosphenytoin | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of fosphenytoin by decreasing its metabolism. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of fosphenytoin if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Galantamine | Possible antagonism of action |
| Halazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, halazepam. |
| Heroin | Cimetidine increases the effect of the narcotic |
| Imipramine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, imipramine, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of imipramine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Itraconazole | The H2-receptor antagonist, cimetidine, may decrease the absorption of itraconazole. |
| Ketazolam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, ketazolam. |
| Ketoconazole | The H2-receptor antagonist, cimetidine, may decrease the absorption of ketoconazole. |
| Labetalol | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of labetolol by decreasing its metabolism. |
| Lidocaine | Increases the effect and toxicity of lidocaine |
| Mephenytoin | Increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Metformin | Cimetidine may increase the therapeutic and adverse effects of metformin by increasing its serum concentration. Consider alternate therapy. |
| Methadone | Cimetidine, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, may increase the serum concentration of metahdone, a CYP3A4 substrate. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of methadone if cimetidine is initiatied, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Metoprolol | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of metoprolol by decreasing its metabolism. |
| Midazolam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, midazolam. |
| Moclobemide | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of moclobemide by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of moclobemide if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Nalbuphine | Increases the effect of the narcotic |
| Nifedipine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Nimodipine | Cimetidine increases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nimodipine. |
| Nitrendipine | Cimetidine increases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nitrendipine. |
| Nortriptyline | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the tricyclic antidepressant, nortriptyline, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of nortriptyline if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Oxtriphylline | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of oxtriphylline by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of oxtriphylline if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Oxycodone | Cimetidine, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, may decrease the metabolism of oxycodone. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of oxycodone if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Oxymorphone | Increases the effect of the narcotic |
| Pazopanib | Affects CYP3A4 metabolism therefore will decrease levels or effect of pazopanib. Consider alternate therapy. |
| Phenytoin | Cimetidine may increase the therapeutic effect of phenytoin. |
| Posaconazole | Significant decrease of posaconazole levels |
| Pramipexole | Cimetidine may increase the effect and toxicity of pramipexole. |
| Prazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, prazepam. |
| Procainamide | The histamine H2-receptor antagonist, cimetidine, may increase the effect of procainamide. |
| Propoxyphene | Cimetidine, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, may decrease the metabolism of propoxyphene. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of propoxyphene if cimetidine is intitiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Propranolol | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of propranolol by decreasing its metabolism. |
| Protriptyline | Cimetidine may increase the effect of tricyclic antidepressant, protriptyline, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of trimipramine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Quazepam | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, quazepam. |
| Quinidine | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of quinidine. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of quinidine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Quinidine barbiturate | Increases the effect of quinidine |
| Rivastigmine | Possible antagonism of action |
| Roflumilast | Increases roflumilast levels. |
| Sildenafil | Increases the effect and toxicity of sildenafil |
| Sufentanil | Increases the effect of the narcotic |
| Tacrine | The metabolism of Tacrine, a CYP1A2 substrate, may be reduced by Cimetidine, a CYP1A2 inhibitors. Monitor the efficacy and toxicity of Tacrine if Cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or if the dose is changed. |
| Tacrolimus | Cimetidine may increase the blood concentration of Tacrolimus. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic/toxic effects of Tacrolimus if Cimetidine therapy is initiated, discontinued or altered. |
| Tamoxifen | Cimetidine may decrease the therapeutic effect of Tamoxifen by decreasing the production of active metabolites. Consider alternate therapy. |
| Tamsulosin | Cimetidine, a CYP3A4/2D6 inhibitor, may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Tamsulosin, a CYP3A4/2D6 substrate. Monitor for changes in therapeutic/adverse effects of Tamsulosin if Cimetidine is initiated, discontinued, or dose changed. |
| Terfenadine | Increased risk of cardiotoxicity and arrhythmias |
| Theophylline | Cimetidine may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Ticlopidine | Cimetidine may increase Ticlopidine levels. Avoid concomitant therapy. |
| Timolol | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of timolol by decreasing its metabolism. |
| Tizanidine | Cimetidine may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Tizanidine. Consider alternate therapy or use caution during co-administration. |
| Tolazoline | Anticipated loss of efficacy of tolazoline |
| Tolterodine | Cimetidine may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Tolterodine. Adjust Tolterodine dose and monitor for efficacy and toxicity. |
| Tramadol | Cimetidine may increase Tramadol toxicity by decreasing Tramadol metabolism and clearance. Cimetidine may decrease the effect of Tramadol by decreasing active metabolite production. |
| Trazodone | The CYP3A4 inhibitor, Cimetidine, may increase Trazodone efficacy/toxicity by decreasing Trazodone metabolism and clearance. Monitor for changes in Trazodone efficacy/toxicity if Cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Triazolam | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of triazolam by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of triazolam if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Trimipramine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of tricyclic antidepressant, trimipramine, by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of trimipramine if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Vilazodone | Cimetidine may decrease the metabolism of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Consider using an alternative H2-antagonist to avoid the risk of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) toxicity. Monitor for increased therapeutic or toxic effects of SSRI if cimetidine is initiated/dose increased, or decreased effects if cimetidine is discontinued/dose decreased. |
| Warfarin | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of warfarin. Monitor for changes in prothrombin time and therapeutic and adverse effects of warfarin if cimetidine is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Zaleplon | Cimetidine may increase the serum concentration of zaleplon by decreasing its metabolism. Reduce the initial dose of zaleplon to 5 mg in patients receiving cimetidine. |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Best effect when taken with food.
- Limit caffeine intake.
