药品详细
Nifedipine(硝苯地平)
化学结构式图
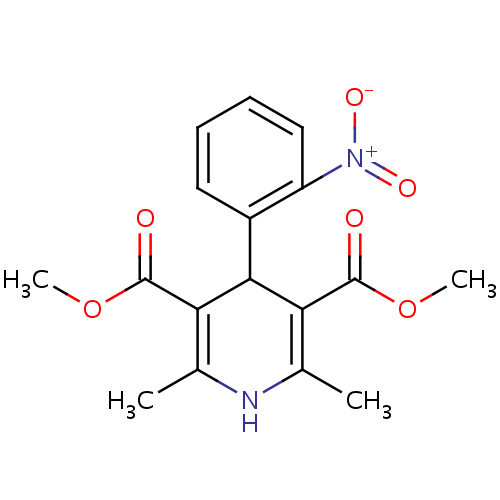
中文名
硝苯地平
英文名
Nifedipine
分子式
C17H18N2O6
化学名
3,5-dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
分子量
Average: 346.3346
Monoisotopic: 346.116486318
Monoisotopic: 346.116486318
CAS号
21829-25-4
ATC分类
C08C 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
Adalat (Bayer);Adalat 10 (Bayer);Adalat 20 (Bayer);Adalat 5 (Bayer);Adalat CC (Bayer);Adalat CR (Bayer);Adalat Crono (Bayer);Adalat Ft (Bayer);Adalat Gits (Bayer);Adalat Gits 30 (Bayer);Adalat LA (Bayer);Adalat LP (Bayer);Adalat Oros (Bayer);Adalat PA (Bayer);Adalat Retard (Bayer);Adalate;Adapine;Adapress;Alat;Aldipin;Alfadal;Alonix;Alonix S;Alpha-Nifedipine Retard;Angipec;Anifed;Anpine;Apo-Nifed;Aprical;Bonacid;Calcibloc;Calcigard;Calcilat;Camont;Cardifen;Cardilat;Cardionorm;Chronadalate;Chronadalate Lp;Citilat;Coracten;Coral;Cordafen;Cordaflex;Cordalat;Cordicant;Cordilan;Cordipin;Corinfar;Corotrend;Corynphar;Depin;Dignokonstant;Dilafed;Dilcor;Dipinkor;Duranifin;Ecodipi;Ecodipin;Ecodipin E;Fedcor;Fedcor Retard;Fenamon;Fenamon Sr;Fenihidin;Fenihidine;Glopir;Hadipin;Hexadilat;Introcar;Kordafen;Macorel;Megalat;Myogard;N1fedilat;Nedipin;Nicardia;Nifangin;Nifar;Nifdemin;Nifebene;Nifecard;Nifecor;Nifedepat;Nifedicor;Nifedin;Nifedine;Nifedipine Retard;Nifedipres;Nifedirex LP;Nifelan;Nifelat;Nifelat Q;Nifelate;Nifensar XL;Nificard;Nifidine;Nifipen;Niphedipine;Orix;Oxcord;Pidilat;Procardia (Pfizer);Procardia XL (Pfizer);Sepamit;Tibricol;Zenusin;
同义名
基本介绍
Nifedipine has been formulated as both a long- and short-acting 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker. It acts primarily on vascular smooth muscle cells by stabilizing voltage-gated L-type calcium channels in their inactive conformation. By inhibiting the influx of calcium in smooth muscle cells, nifedipine prevents calcium-dependent myocyte contraction and vasoconstriction. A second proposed mechanism for the drug’s vasodilatory effects involves pH-dependent inhibition of calcium influx via inhibition of smooth muscle carbonic anhydrase. Nifedipine is used to treat hypertension and chronic stable angina.
生产厂家
- Actavis elizabeth llc
- Actavis southatlantic llc
- Bayer healthcare pharmaceuticals inc
- Bayer pharmaceuticals corp
- Biovail laboratories inc
- Catalent pharma solutions llc
- Chase laboratories inc
- Intergel pharmaceutical inc
- Martec usa llc
- Mylan pharmaceuticals inc
- Osmotica pharmaceutical corp
- Pfizer inc
- Pfizer laboratories div pfizer inc
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa inc
- Watson laboratories inc
封装厂家
- Actavis Group
- Amerisource Health Services Corp.
- Apotheca Inc.
- A-S Medication Solutions LLC
- Atlantic Biologicals Corporation
- Bayer Healthcare
- Biovail Pharmaceuticals
- Bryant Ranch Prepack
- Cardinal Health
- Caremark LLC
- Catalent Pharma Solutions
- Comprehensive Consultant Services Inc.
- Coupler Enterprises Inc.
- Dept Health Central Pharmacy
- DHHS Program Support Center Supply Service Center
- Direct Dispensing Inc.
- Dispensing Solutions
- Diversified Healthcare Services Inc.
- Elan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Eurand Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Gavis Pharmaceuticals LLC
- Giant Food Inc.
- Goldline Laboratories Inc.
- Greenstone LLC
- H.E. Butt Grocery Co.
- H.J. Harkins Co. Inc.
- Heartland Repack Services LLC
- International Laboratories Inc.
- Ivax Pharmaceuticals
- IVC Industries Inc.
- Kaiser Foundation Hospital
- LeaderPharma
- Liberty Pharmaceuticals
- Major Pharmaceuticals
- Mason Distributors
- Mckesson Corp.
- Medisca Inc.
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
- Mylan
- Neuman Distributors Inc.
- Novopharm Ltd.
- Nucare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Palmetto Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Pharmaceutical Utilization Management Program VA Inc.
- Pharmacy Service Center
- Pharmedix
- Physicians Total Care Inc.
- Prasco Labs
- Pratt Pharmaceuticals
- Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Prepackage Specialists
- Prepak Systems Inc.
- Qualitest
- Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Redpharm Drug
- Remedy Repack
- Resource Optimization and Innovation LLC
- RP Scherer Canada Inc.
- Sandhills Packaging Inc.
- Schering Corp.
- Schwarz Pharma Inc.
- Southwood Pharmaceuticals
- Talbert Medical Management Corp.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Tya Pharmaceuticals
- UDL Laboratories
- United Research Laboratories Inc.
- Va Cmop Dallas
- Vangard Labs Inc.
- Warrick Pharmaceuticals Corp.
- Watson Pharmaceuticals
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
;Angina Pectoris 心绞痛;ANTIHYPERTENSIVES 降血压;
药理
| Indication | For the management of vasospastic angina, chronic stable angina, hypertension, and Raynaud's phenomenon. May be used as a first line agent for left ventricular hypertrophy and isolated systolic hypertension (long-acting agents). | ||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Nifedipine, the prototype of the dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blockers (CCBs), is similar to other dihydropyridines including amlodipine, felodipine, isradipine, and nicardipine. There are at least five different types of calcium channels in Homo sapiens: L-, N-, P/Q-, R- and T-type. CCBs target L-type calcium channels, the major channel in muscle cells that mediates contraction. Similar to other DHP CCBs, nifedipine binds directly to inactive calcium channels stabilizing their inactive conformation. Since arterial smooth muscle depolarizations are longer in duration than cardiac muscle depolarizations, inactive channels are more prevalent in smooth muscle cells. Alternative splicing of the alpha-1 subunit of the channel gives nifedipine additional arterial selectivity. At therapeutic sub-toxic concentrations, nifedipine has little effect on cardiac myocytes and conduction cells. By blocking the calcium channels, Nifedipine inhibits the spasm of the coronary artery and dilates the systemic arteries, results in a increase of myocardial oxygen supply and a decrease in systemic blood pressure. | ||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Nifedipine decreases arterial smooth muscle contractility and subsequent vasoconstriction by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions through L-type calcium channels. Calcium ions entering the cell through these channels bind to calmodulin. Calcium-bound calmodulin then binds to and activates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK). Activated MLCK catalyzes the phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain subunit of myosin, a key step in muscle contraction. Signal amplification is achieved by calcium-induced calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through ryanodine receptors. Inhibition of the initial influx of calcium inhibits the contractile processes of smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload. The vasodilatory effects of nifedipine result in an overall decrease in blood pressure. | ||||||||
| Absorption | Rapidly and fully absorbed following oral administration. | ||||||||
| Volume of distribution | Not Available | ||||||||
| Protein binding | 92-98% | ||||||||
| Metabolism |
Hepatic metabolism via cytochrome P450 system. Predominantly metabolized by CYP3A4, but also by CYP1A2 and CYP2A6 isozymes.
Important The metabolism module of DrugBank is currently in beta. Questions or suggestions? Please contact us.
|
||||||||
| Route of elimination | Nifedipine is extensively metabolized to highly water-soluble, inactive metabolites accounting for 60 to 80% of the dose excreted in the urine. The remainder is excreted in the feces in metabolized form, most likely as a result of biliary excretion. | ||||||||
| Half life | 2 hours | ||||||||
| Clearance | Not Available | ||||||||
| Toxicity | Symptoms of overdose include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, severe drop in blood pressure, slurred speech, and weakness. LD50=494 mg/kg (orally in mice); LD50=1022 mg/kg (orally in rats) | ||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||
| Pathways |
|
||||||||
理化性质
| Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Amobarbital | The barbiturate, amobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Aprobarbital | The barbiturate, aprobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Butabarbital | The barbiturate, butabarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Butalbital | The barbiturate, butalbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Butethal | The barbiturate, butethal, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Cimetidine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Cisapride | Cisapride may increase the effect and toxicity of nifedipine. |
| Cyclosporine | Increased risk of gingivitis |
| Dihydroquinidine barbiturate | Decreased quinidine effect, increased nifedipine effect |
| Etravirine | Nifedipine, when used concomitantly with etravirine (a strong CYP3A4 inducer), may experience a decrease in serum concentration. It is recommended to monitor nifedipine therapy for reduced effectiveness. |
| Ginseng | Ginseng increases the effect and toxicity of nifedipine |
| Heptabarbital | The barbiturate, heptabarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Hexobarbital | The barbiturate, hexobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Imatinib | Imatinib increases the effect and toxicity of nifedipine |
| Melatonin | Melatonin can possibly decrease the effect of nifedipine |
| Methohexital | The barbiturate, methohexital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Methylphenobarbital | The barbiturate, methylphenobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Pentobarbital | The barbiturate, pentobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Phenobarbital | The barbiturate, phenobarbital, may decrease the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Primidone | The barbiturate, primidone, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Quinidine | Decreased quinidine effect, increased nifedipine effect |
| Quinidine barbiturate | Decreased quinidine effect, increased nifedipine effect |
| Quinupristin | Synercid increases the effect of ziprasidone |
| Rifampin | Rifampin decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Secobarbital | The barbiturate, secobarbital, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| St. John's Wort | St. John's Wort decreases the effect of nifedipine |
| Tacrine | The metabolism of Tacrine, a CYP1A2 substrate, may be reduced by Nifedipine, a CYP1A2 inhibitors. Monitor the efficacy and toxicity of Tacrine if Nifedipine is initiated, discontinued or if the dose is changed. |
| Tacrolimus | The calcium channel blocker, Nifedipine, may increase the blood concentration of Tacrolimus. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic/toxic effects of Tacrolimus if Nifedipine therapy is initiated, discontinued or altered. |
| Talbutal | The barbiturate, talbutal, decreases the effect of the calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. |
| Telithromycin | Telithromycin may reduce clearance of Nifedipine. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in the therapeutic/adverse effects of Nifedipine if Telithromycin is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Thiopental | The CYP3A4 inducer, Thiopental, may increase the metabolism and clearance of Nifedipine, a CYP3A4 substrate. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic/adverse effects of Nifedipine if Thiopental is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Tipranavir | Tipranavir may decrease the metabolism and clearance of the calcium channel blocker, Nifedipine. Monitor for changes in Nifedipine therapeutic and adverse effects if Tipranavir is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Tizanidine | Nifedipine may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Tizanidine. Consider alternate therapy or use caution during co-administration. |
| Treprostinil | Additive hypotensive effect. Monitor antihypertensive therapy during concomitant use. |
| Voriconazole | Voriconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, may increase the serum concentration of nifedipine by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of nifedipine if voriconazole is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Avoid natural licorice.
- Grapefruit down-regulates post-translational expression of CYP3A4, the major metabolizing enzyme of nifedipine. Grapefruit, in all forms (e.g. whole fruit, juice and rind), can significantly increase serum levels of nifedipine and may cause toxicity. Avoid grapefruit products while on this medication.
- Take with low fat meal.
