药品详细
Tranexamic Acid(氨甲环酸)
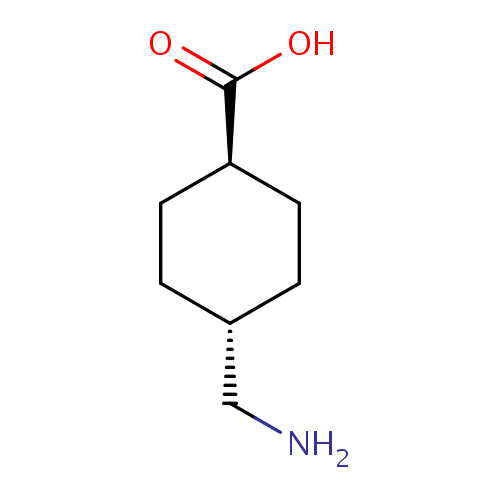
化学结构式图
中文名
氨甲环酸
英文名
Tranexamic Acid
分子式
C8H15NO2
化学名
(1r,4r)-4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid
分子量
Average: 157.2102
Monoisotopic: 157.110278729
Monoisotopic: 157.110278729
CAS号
1197-18-8
ATC分类
B02A 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
同义名
基本介绍
Antifibrinolytic hemostatic used in severe hemorrhage. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Ferring pharmaceuticals as
- Pharmacia and upjohn co
封装厂家
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference | Not Available |
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes | Not Available |
| Substructures | Not Available |
适应症
药理
| Indication | For use in patients with hemophilia for short term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction. It can also be used for excessive bleeding in menstruation, surgery, or trauma cases. | ||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic that competitively inhibits the activation of plasminogen to plasmin. Tranexamic acid is a competitive inhibitor of plasminogen activation, and at much higher concentrations, a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin, i.e., actions similar to aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid is about 10 times more potent in vitro than aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. Tranexamic acid in a concentration of 1 mg per mL does not aggregate platelets in vitro. In patients with hereditary angioedema, inhibition of the formation and activity of plasmin by tranexamic acid may prevent attacks of angioedema by decreasing plasmin-induced activation of the first complement protein (C1). | ||||||
| Mechanism of action | Tranexamic acid competitively inhibits activation of plasminogen (via binding to the kringle domain), thereby reducing conversion of plasminogen to plasmin (fibrinolysin), an enzyme that degrades fibrin clots, fibrinogen, and other plasma proteins, including the procoagulant factors V and VIII. Tranexamic acid also directly inhibits plasmin activity, but higher doses are required than are needed to reduce plasmin formation. | ||||||
| Absorption | Absorption of tranexamic acid after oral administration in humans represents approximately 30 to 50% of the ingested dose and bioavailability is not affected by food intake. | ||||||
| Volume of distribution |
|
||||||
| Protein binding | The plasma protein binding of tranexamic acid is about 3% at therapeutic plasma levels and seems to be fully accounted for by its binding to plasminogen (does not bind serum albumin). | ||||||
| Metabolism |
Only a small fraction of the drug is metabolized (less than 5%).
|
||||||
| Route of elimination | Urinary excretion is the main route of elimination via glomerular filtration. | ||||||
| Half life | Biological half-life in the joint fluid is about 3 hours. | ||||||
| Clearance |
|
||||||
| Toxicity | Oral LD50 in mice is >10 gm/kg. Symptoms of overdosage may be nausea, vomiting, orthostatic symptoms and/or hypotension. | ||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||
| Pathways |
|
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
食物相互作用
Not Available
