药品详细
Acetohexamide(醋磺)
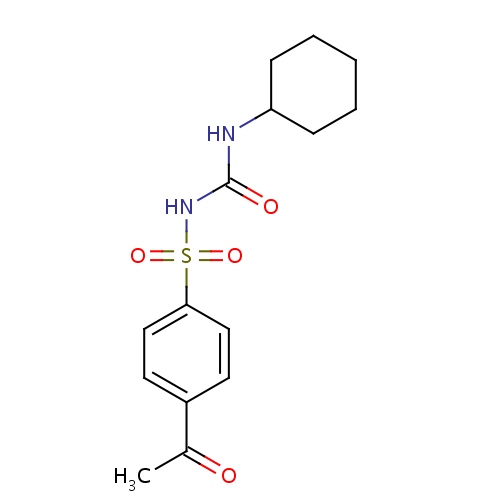
化学结构式图
中文名
醋磺
英文名
Acetohexamide
分子式
C15H20N2O4S
化学名
1-[(4-acetylbenzene)sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea
分子量
Average: 324.395
Monoisotopic: 324.114377828
Monoisotopic: 324.114377828
CAS号
968-81-0
ATC分类
A10B Oral Blood Glucose Lowering Drugs, Excl. Insulins
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
Cyclamide;Dimelin;Dimelor;Dymelor;Gamadiabet;Hypoglicil;Metaglucina;Minoral;Ordimel;Tsiklamid;
同义名
Acetohexamid;
基本介绍
A sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agent that is metabolized in the liver to 1-hydrohexamide. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Barr laboratories inc
- Eli lilly industries inc
- Usl pharma inc
- Watson laboratories inc
封装厂家
- Barr Pharmaceuticals
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference | Not Available |
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
Diabetes 糖尿病;
药理
| Indication | Used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2 (adult-onset). | ||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Acetohexamide is an intermediate-acting, first-generation oral sulfonylurea. It lowers blood sugar by stimulating the pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin and by helping the body use insulin efficiently. The pancreas must produce insulin for this medication to work. Acetohexamide has one-third the potency of chlorpropamide, and twice the potency of tolbutamide; however, similar hypoglycemic efficacy occurs with equipotent dosage of sulfonylureas. | ||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Sulfonylureas such as acetohexamide bind to an ATP-dependent K+ channel on the cell membrane of pancreatic beta cells. This inhibits a tonic, hyperpolarizing outflux of potassium, which causes the electric potential over the membrane to become more positive. This depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. The rise in intracellular calcium leads to increased fusion of insulin granulae with the cell membrane, and therefore increased secretion of (pro)insulin. | ||||||||
| Absorption | Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract. | ||||||||
| Volume of distribution | Not Available | ||||||||
| Protein binding | 90% | ||||||||
| Metabolism |
Extensively metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite hydroxyhexamide, which exhibits greater hypoglycemic potency than acetohexamide. Hydroxyhexamide is believed to be responsible for prolonged hypoglycemic effects.
Important The metabolism module of DrugBank is currently in beta. Questions or suggestions? Please contact us.
|
||||||||
| Route of elimination | Not Available | ||||||||
| Half life | Elimination half-life of the parent compound is 1.3 hours and the elimination half-life of the active metabolite is approximately 5-6 hours. | ||||||||
| Clearance | Not Available | ||||||||
| Toxicity | Oral, rat LD50: 5 gm/kg; Oral, mouse LD50: >2500 mg/kg. Symptoms of an acetohexamide overdose include hunger, nausea, anxiety, cold sweats, weakness, drowsiness, unconsciousness, and coma. | ||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Acebutolol | Acebutolol may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia and increase the time required for the body to compensate for hypoglycemia. |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | Acetylsalicylic acid increases the effect of sulfonylurea, acetohexamide. |
| Atenolol | The beta-blocker, atenolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Betaxolol | The beta-blocker, betaxolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Bisoprolol | The beta-blocker, bisoprolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Carteolol | The beta-blocker, carteolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Carvedilol | The beta-blocker, carvedilol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Chloramphenicol | Chloramphenicol may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, acetohexamide. |
| Clofibrate | Clofibrate may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, acetohexamide. |
| Dicumarol | Dicumarol may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, acetohexamide. |
| Esmolol | The beta-blocker, esmolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Labetalol | The beta-blocker, labetalol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Metoprolol | The beta-blocker, metoprolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Nadolol | The beta-blocker, nadolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Oxprenolol | The beta-blocker, oxprenolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Phenylbutazone | Phenylbutazone may increase the effect of acetohexamide. |
| Pindolol | The beta-blocker, pindolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Practolol | The beta-blocker, practolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Propranolol | The beta-blocker, propranolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Rifampin | Rifampin may decrease the effect of sulfonylurea, acetohexamide. |
| Sotalol | The beta-blocker, sotalol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Timolol | The beta-blocker, timolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Take without regard to meals.