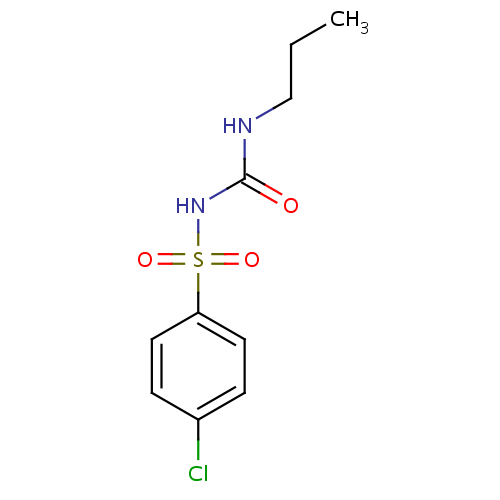
Chlorpropamide(氯磺丙脲)
Monoisotopic: 276.033540689
Chlorpropamide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It belongs to the sulfonylurea class of insulin secretagogues, which act by stimulating β cells of the pancreas to release insulin. Sulfonylureas increase both basal insulin secretion and meal-stimulated insulin release. Medications in this class differ in their dose, rate of absorption, duration of action, route of elimination and binding site on their target pancreatic β cell receptor. Sulfonylureas also increase peripheral glucose utilization, decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis and may increase the number and sensitivity of insulin receptors. Sulfonylureas are associated with weight gain, though less so than insulin. Due to their mechanism of action, sulfonylureas may cause hypoglycemia and require consistent food intake to decrease this risk. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased in elderly, debilitated and malnourished individuals. Chlorpropamide is not recommended for the treatment of NIDDM as it increases blood pressure and the risk of retinopathy (UKPDS-33). Up to 80% of the single oral dose of chlorpropramide is metabolized, likely in the liver; 80-90% of the dose is excreted in urine as unchanged drug and metabolites. Renal and hepatic dysfunction may increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Barr laboratories inc
- Clonmel healthcare ltd
- Duramed pharmaceuticals inc sub barr laboratories inc
- Halsey drug co inc
- Ivax pharmaceuticals inc
- Mylan pharmaceuticals inc
- Par pharmaceutical inc
- Pfizer laboratories div pfizer inc
- Pliva inc
- Sandoz inc
- Superpharm corp
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa inc
- Usl pharma inc
- Watson laboratories inc
- Central Texas Community Health Centers
- Direct Dispensing Inc.
- Dispensing Solutions
- H and H Laboratories
- Major Pharmaceuticals
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
- Mylan
- Nucare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- PCA LLC
- PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Pharmedix
- Physicians Total Care Inc.
- Pliva Inc.
- Prepackage Specialists
- Prescript Pharmaceuticals
- Qualitest
- UDL Laboratories
- Wyeth Pharmaceuticals
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference | Not Available |
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
| Indication | For treatment of NIDDM in conjunction with diet and exercise. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Chlorpropamide, a second-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent, is used with diet to lower blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus type II. Chlorpropamide is twice as potent as the related second-generation agent glipizide. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Sulfonylureas such as chlorpropamide bind to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the pancreatic cell surface, reducing potassium conductance and causing depolarization of the membrane. Depolarization stimulates calcium ion influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels, raising intracellular concentrations of calcium ions, which induces the secretion, or exocytosis, of insulin. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption | Readily absorbed from the GI tract. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 2-4 hours and the onset of action occurs within one hour. The maximal effect of chlorpropamide is seen 3-6 hours following oral administration. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume of distribution | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein binding | Highly bound to plasma proteins. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism |
Up to 80% of dose is metabolized likely through the liver to to 2-hydroxylchlorpropamide (2-OH CPA), p-chlorobenzenesulfonylurea (CBSU), 3-hydroxylchlorpropamide (3-OH CPA), and p-chlorobenzenesulfonamide (CBSA); CBSA may be produced by decomposition in urine. It is unknown whether chlorpropamide metabolites exert hypoglycemic effects.
Important The metabolism module of DrugBank is currently in beta. Questions or suggestions? Please contact us.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of elimination | 80-90% of a single oral dose is excreted in the urine as unchaged drug and metabolites within 96 hours. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Half life | Approximately 36 hours with interindividual variation ranging from 25-60 hours. Duration of effect persists for at least 24 hours. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity | IPN-RAT LD50 580 mg/kg | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Acebutolol | Acebutolol may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia and increase the time required for the body to compensate for hypoglycemia. |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | Acetylsalicylic acid may increase the effect of the sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Atenolol | The beta-blocker, atenolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Betaxolol | The beta-blocker, betaxolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Bevantolol | The beta-blocker, bevantolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Bisoprolol | The beta-blocker, bisoprolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Carteolol | The beta-blocker, carteolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Carvedilol | The beta-blocker, carvedilol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Chloramphenicol | Chloramphenicol may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Clofibrate | Clofibrate may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Diazoxide | Antagonism. |
| Dicumarol | Dicumarol may increase the effect of sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Esmolol | The beta-blocker, esmolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Glucosamine | Possible hyperglycemia |
| Labetalol | The beta-blocker, labetalol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Metoprolol | The beta-blocker, metoprolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Nadolol | The beta-blocker, nadolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Oxprenolol | The beta-blocker, oxprenolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Penbutolol | The beta-blocker, penbutolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Phenylbutazone | Phenylbutazone increases the effect of the hypoglycemic agent |
| Pindolol | The beta-blocker, pindolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Practolol | The beta-blocker, practolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Propranolol | The beta-blocker, propranolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Rifampin | Rifampin may decrease the effect of sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Salsalate | The salicylate, salsalate, increases the effect of the sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Somatropin recombinant | Somatropin may antagonize the hypoglycemic effect of chlorpropamide. Monitor for changes in fasting and postprandial blood sugars. |
| Sotalol | The beta-blocker, sotalol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Sulfacytine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfadiazine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfadoxine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfamerazine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfamethazine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfamethizole | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfamethoxazole | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfapyridine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfasalazine | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Sulfisoxazole | Sulfonamide/sulfonylurea: possible hypoglycemia |
| Timolol | The beta-blocker, timolol, may decrease symptoms of hypoglycemia. |
| Trisalicylate-choline | The salicylate, trisalicylate-choline, increases the effect of the sulfonylurea, chlorpropamide. |
| Voriconazole | Additive QTc prolongation may occur. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for QTc prolongation as this can lead to Torsade de Pointes (TdP). |
- Avoid alcohol.
- Food reduces the rate of absorption.
- Take 30 minutes before meal.