药品详细
Omeprazole(奥美拉唑)
化学结构式图
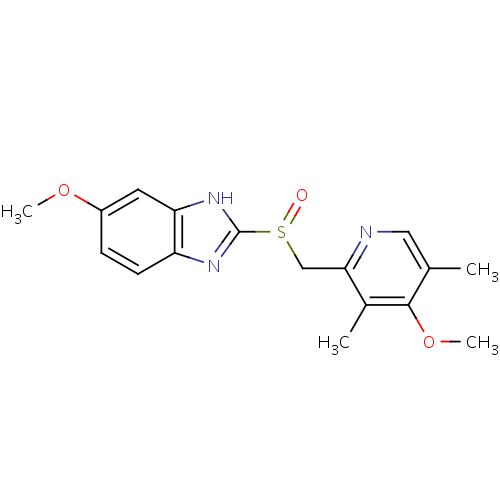
中文名
奥美拉唑
英文名
Omeprazole
分子式
C17H19N3O3S
化学名
6-methoxy-2-{[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methane]sulfinyl}-1H-1,3-benzodiazole
分子量
Average: 345.416
Monoisotopic: 345.114712179
Monoisotopic: 345.114712179
CAS号
73590-58-6
ATC分类
A02B 未知;A02B 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
Antra;Audazol;Aulcer;Belmazol;Ceprandal;Danlox;Demeprazol;Desec;Dizprazol;Dudencer;Elgam;Emeproton;Epirazole;Erbolin;Exter;Gasec;Gastrimut;Gastroloc;Gibancer;Indurgan;Inhibitron;Inhipump;Lensor;Logastric;Lomac;Losec;Mepral;Miol;Miracid;Mopral;Morecon;Nilsec;Nopramin;Ocid;Olexin;Omapren;Omebeta 20;Omed;Omegast;Omepral;Omeprazon;Omeprol;Omesek;Omezol;Omezolan;Omid;Omisec;Omizac;Ompanyt;Ortanol;Osiren;Ozoken;Paprazol;Parizac;Pepticum;Pepticus;Peptilcer;Prazentol;Prazidec;Prazolit;Prilosec;Procelac;Proclor;Prysma;Ramezol;Regulacid;Result;Sanamidol;Secrepina;Tedec Ulceral;Ulceral;Ulcesep;Ulcometion;Ulcozol;Ulcsep;Ulsen;Ultop;Ulzol;Victrix;Zefxon;Zegerid;Zepral;Zimor;Zoltum;
同义名
OMEP;Omeprazol [INN-Spanish];omeprazole;Omeprazole magnesium;Omeprazolum [INN-Latin];OMP;OMZ;
基本介绍
A highly effective inhibitor of gastric acid secretion used in the therapy of stomach ulcers and zollinger-ellison syndrome. The drug inhibits the H()-K()-ATPase (H()-K()-exchanging ATPase) in the proton pump of gastric parietal cells. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Apotex inc
- Astrazeneca lp
- Dexcel pharma technologies ltd
- Dr reddys laboratories ltd
- Impax laboratories inc
- Kremers urban development co
- Lek pharmaceuticals d d
- Mylan pharmaceuticals inc
- Sandoz inc
- Santarus, Inc.
- Watson laboratories inc florida
封装厂家
- Aidarex Pharmacuticals LLC
- Altura Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Amerisource Health Services Corp.
- Apotex Inc.
- A-S Medication Solutions LLC
- Astra Pharma Inc.
- AstraZeneca Inc.
- Atlantic Biologicals Corporation
- Blenheim Pharmacal
- Bryant Ranch Prepack
- Cardinal Health
- Caremark LLC
- Comprehensive Consultant Services Inc.
- Concern Stirol
- Contract Packaging Resources Inc.
- Corepharma LLC
- Coupler Enterprises Inc.
- CVS Pharmacy
- Dept Health Central Pharmacy
- Dexcel Ltd.
- DHHS Program Support Center Supply Service Center
- Dispensing Solutions
- Diversified Healthcare Services Inc.
- Doctor Reddys Laboratories Ltd.
- Ftl International Inc.
- Global Pharmaceuticals
- Golden State Medical Supply Inc.
- H.J. Harkins Co. Inc.
- Heartland Repack Services LLC
- Impax Laboratories Inc.
- Innoviant Pharmacy Inc.
- Kaiser Foundation Hospital
- Keltman Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Laboratorios Dr Esteve SA
- Lake Erie Medical and Surgical Supply
- Lek Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Major Pharmaceuticals
- Mckesson Corp.
- Medisca Inc.
- Medsource Pharmaceuticals
- Merck & Co.
- Merial Inc.
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
- Mylan
- Nucare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Palmetto Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Par Pharmaceuticals
- Patheon Inc.
- PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Perrigo Co.
- Physicians Total Care Inc.
- Preferred Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Prepak Systems Inc.
- Prescript Pharmaceuticals
- Procter & Gamble
- Ranbaxy Laboratories
- Rebel Distributors Corp.
- Remedy Repack
- S&P Healthcare
- Sandhills Packaging Inc.
- Sandoz
- Santarus Inc.
- Schwarz Pharma Inc.
- Southwood Pharmaceuticals
- St Mary's Medical Park Pharmacy
- Stat Rx Usa
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Torpharm Inc.
- UDL Laboratories
- Vangard Labs Inc.
- Watson Pharmaceuticals
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
gastric acid RELATED DISORDERS 中和胃酸;
药理
| Indication | For the treatment of acid-reflux disorders (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, H. pylori eradication, and prevention of gastroinetestinal bleeds with NSAID use. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Omeprazole is a compound that inhibits gastric acid secretion and is indicated in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), the healing of erosive esophagitis, and H. pylori eradication to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence. Omeprazole belongs to a new class of antisecretory compounds, the substituted benzimidazoles, that do not exhibit anticholinergic or H2 histamine antagonistic properties, but that suppress gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+ ATPase at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell. As a result, it inhibits acid secretion into the gastric lumen. This effect is dose-related and leads to inhibition of both basal and stimulated acid secretion irrespective of the stimulus. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor that suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase in the gastric parietal cell. By acting specifically on the proton pump, omeprazole blocks the final step in acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption | Absorption is rapid, absolute bioavailability (compared to intravenous administration) is about 30-40% at doses of 20-40 mg. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume of distribution | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein binding | 95% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism |
Hepatic.
Important The metabolism module of DrugBank is currently in beta. Questions or suggestions? Please contact us.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of elimination | Urinary excretion is a primary route of excretion of omeprazole metabolites. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Half life | 0.5-1 hour | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clearance |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity | Symptoms of overdose include confusion, drowsiness, blurred vision, tachycardia, nausea, diaphoresis, flushing, headache, and dry mouth. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Alprazolam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, alprazolam. |
| Atazanavir | This gastric pH modifier decreases the levels/effects of atazanavir |
| Avanafil | Nineteen healthy male volunteers received a single 40 omeprazole delayed-release capsule once daily for 8 days (Days 1-8), and a single 200 mg avanafil on Day 8. Twelve hour pharmacokinetics of omeprazole on Days 7 and 8 were compared. Co-administration with avanafil resulted in an approximate 5.9% increase in AUC0-inf and 8.6% increase in Cmax of omeprazole. |
| Bendamustine | Affects hepatic CYP1A2 metabolism, thus increasing bendamustine levels. Concentration of active metabolites may be decreased due to decreased conversion. |
| Cefditoren | Proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole may decrease the serum concentration of cefditoren. If possible, avoid use of cefditoren with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Consider alternative methods to minimize/control acid reflux (eg, diet modification) or alternative antimicrobial therapy if use of PPIs can not be avoided. |
| Chlordiazepoxide | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, chlordiazepoxide. |
| Cilostazol | Omeprazole increases the effect of cilostazol |
| Clonazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, clonazepam. |
| Clopidogrel | Omeprazole may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of clopidogrel. Clopidogrel prescribing information recommends avoiding concurrent use with omeprazole, due to the possibility that combined use may result in decreased clopidogrel effectiveness. |
| Clorazepate | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, clorazepate. |
| Cyclosporine | Omeprazole increases the effect and toxicity of cyclosporine |
| Dasatinib | Omeprazole may decrease the serum level of dasatinib. |
| Diazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, diazepam. |
| Disopyramide | The beta-blocker increases toxicity of disopyramide |
| Enoxacin | Omeprazole may decrease the absorption of enoxacin. |
| Estazolam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, estazolam. |
| Ethotoin | Omeprazole increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Flurazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, flurazepam. |
| Fosphenytoin | Omeprazole increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Halazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, halazepam. |
| Indinavir | Omeprazole decreases the absorption of indinavir |
| Itraconazole | The proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole, may decrease the absorption of itraconazole. |
| Ketazolam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, ketazolam. |
| Ketoconazole | The proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole, may decrease the absorption of ketoconazole. |
| Mephenytoin | Omeprazole increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Methotrexate | Omeprazole increases the levels of methotrexate |
| Midazolam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, midazolam. |
| Ospemifene | Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitors may increase levels of ospemifene. Monitor concomitant therapy closely. |
| Phenytoin | Omeprazole increases the effect of hydantoin |
| Prazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, prazepam. |
| Quazepam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, quazepam. |
| Rilpivirine | Proton-pump inhibitors increase gastric pH which causes a decrease in the exposure of rilpivirine thus reducing efficacy. |
| Roflumilast | Affects CYP1A2 metabolism; decreases level or effect of roflumilast. |
| St. John's Wort | St. John's Wort decreases the levels/effects of omeprazole |
| Tacrolimus | Omeprazole may increase the blood concentration of Tacrolimus. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic/toxic effects of Tacrolimus if Omeprazole therapy is initiated, discontinued or altered. |
| Tipranavir | Tipranavir, co-administered with Ritonavir, may decrease the plasma concentration of Omeprazole. Consider alternate therapy or increase the dose of Omeprazole based on the therapeutic response. |
| Tocilizumab | Omeprazole is a CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 substrate. Exposure of omeprazole decreases following administration of tocilizumab.. |
| Triazolam | Omeprazole may increase the effect of the benzodiazepine, triazolam. |
| Trimipramine | The strong CYP2C19 inhibitor, Omeprazole, may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Trimipramine, a CYP2C19 substrate. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in therapeutic and adverse effects of Trimipramine if Omeprazole is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Vismodegib | Vismodegib serum concentrations may be decreased by proton pump inhibitors such as omeprazole. |
| Voriconazole | Voriconazole increases the effect and toxicity of omeprazole |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Take 30-60 minutes before meals.
