药品详细
Leflunomide (来氟米特 )
化学结构式图
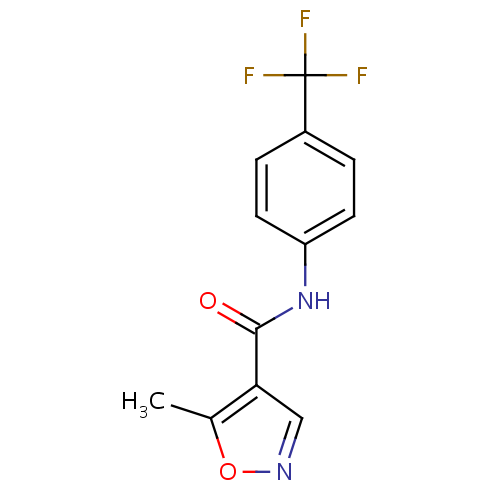
中文名
来氟米特
英文名
Leflunomide
分子式
Not Available
化学名
5-methyl-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamide
分子量
Average: 270.2073
Monoisotopic: 270.061612157
Monoisotopic: 270.061612157
CAS号
75706-12-6
ATC分类
L04A 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
商品名
Arava;
同义名
leflunomide;Leflunomidum [INN-Latin];Lefunomide [INN-Spanish];
基本介绍
Leflunomide is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor belonging to the DMARD (disease-modifying antirheumatic drug) class of drugs, which are chemically and pharmacologically very heterogeneous. Leflunomide was approved by FDA and in many other countries (e.g., Canada, Europe) in 1999.
生产厂家
- Apotex inc etobicoke site
- Barr laboratories inc
- Par pharmaceutical inc
- Sandoz inc
- Sanofi aventis us llc
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa
封装厂家
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
| Form | Route | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Tablet | Oral |
规格
| Unit description | Cost | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Arava 10 mg tablet | 24.76 USD | tablet |
| Arava 20 mg tablet | 24.76 USD | tablet |
| Leflunomide 10 mg tablet | 16.75 USD | tablet |
| Leflunomide 20 mg tablet | 16.75 USD | tablet |
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE 免疫抑制;
药理
| Indication | For the management of the signs and symptoms of active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) to improve physical function and to slow the progression of structural damage associated with the disease. Has also been used for the prevention of acute and chronic rejection in recipients of solid organ trasnplants and is designated by the FDA as an orphan drug for this use. | ||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Leflunomide is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor indicated in adults for the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is an auto-immune disease characterized by high T-cell activity. T cells have two pathways to synthesize pyrimidines: the salvage pathways and the de novo synthesis. At rest, T lymphocytes meet their metabolic requirements by the salvage pathway. Activated lymphocytes need to expand their pyrimidine pool 7- to 8-fold, while the purine pool is expanded only 2- to 3-fold. To meet the need for more pyrimidines, activated T cells use the de novo pathway for pyrimidine synthesis. Therefore, activated T cells, which are dependent on de novo pyrimidine synthesis, will be more affected by leflunomide's inhibition of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase than other cell types that use the salvage pathway of pyrimidine synthesis. | ||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Leflunomide is a prodrug that is rapidly and almost completely metabolized following oral administration to its pharmacologically active metabolite, A77 1726. This metabolite is responsible for essentially all of the drug's activity in-vivo. The mechanism of action of leflunomide has not been fully determined, but appears to primarily involve regulation of autoimmune lymphocytes. It has been suggested that leflunomide exerts its immunomodulating effects by preventing the expansion of activated autoimmune lymphocytes via interferences with cell cycle progression. In-vitro data indicates that leflunomide interferes with cell cycle progression by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (a mitochondrial enzyme involved in de novo pyrimidine ribonucleotide uridine monophosphate (rUMP)synthesis) and has antiproliferative activity. Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase consists of 2 domains: an 伪/尾-barrel domain containing the active site and an 伪-helical domain that forms a tunnel leading to the active site. A77 1726 binds to the hydrophobic tunnel at a site near the flavin mononucleotide. Inhibition of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase by A77 1726 prevents production of rUMP by the de novo pathway; such inhibition leads to decreased rUMP levels, decreased DNA and RNA synthesis, inhibition of cell proliferation, and G1 cell cycle arrest. It is through this action that leflunomide inhibits autoimmune T-cell proliferation and production of autoantibodies by B cells. Since salvage pathways are expected to sustain cells arrested in the G1 phase, the activity of leflunomide is cytostatic rather than cytotoxic. Other effects that result from reduced rUMP levels include interference with adhesion of activated lymphocytes to the synovial vascular endothelial cells, and increased synthesis of immunosuppressive cytokines such as transforming growth factor-尾 (TGF-尾). Leflunomide is also a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Tyrosine kinases activate signalling pathways leading to DNA repair, apoptosis and cell proliferation. Inhibition of tyrosine kinases can help to treating cancer by preventing repair of tumor cells. | ||||||||||
| Absorption | Well absorbed, peak plasma concentrations appear 6-12 hours after dosing | ||||||||||
| Volume of distribution |
|
||||||||||
| Protein binding | >99.3% | ||||||||||
| Metabolism |
Primarily hepatic. Leflunomide is converted to its active form following oral intake.
|
||||||||||
| Route of elimination | The active metabolite is eliminated by further metabolism and subsequent renal excretion as well as by direct biliary excretion. In a 28 day study of drug elimination (n=3) using a single dose of radiolabeled compound, approximately 43% of the total radioactivity was eliminated in the urine and 48% was eliminated in the feces. It is not known whether leflunomide is excreted in human milk. Many drugs are excreted in human milk, and there is a potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from leflunomide. | ||||||||||
| Half life | 2 weeks | ||||||||||
| Clearance | Not Available | ||||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50=100-250 mg/kg (acute oral toxicity) | ||||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available |
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 165-166 oC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Acenocoumarol | Leflunomide may increase the anticoagulant effect of acenocoumarol. |
| Anisindione | Leflunomide may increase the anticoagulant effect of anisindione. |
| Dicumarol | Leflunomide may increase the anticoagulant effect of dicumarol. |
| Rifampin | Rifampin increases the effect of leflunomide |
| Vinblastine | Vinblastine may increase the adverse/toxic effects of Leflunomide. This may increase the risk of hematologic toxicities such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia. In patients receiving Vinblastine, consider eliminating the loading dose of Leflunomide. Monitor for bone marrow suppression at least monthly during concomitant therapy. |
| Vincristine | Vincristine may increase the adverse/toxic effects of Leflunomide. This may increase the risk of hematologic toxicities such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia. In patients receiving Vincristine, consider eliminating the loading dose of Leflunomide. Monitor for bone marrow suppression at least monthly during concomitant therapy. |
| Vinorelbine | Vinorelbine may increase the adverse/toxic effects of Leflunomide. This may increase the risk of hematologic toxicities such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia. In patients receiving Vinorelbine, consider eliminating the loading dose of Leflunomide. Monitor for bone marrow suppression at least monthly during concomitant therapy. |
| Warfarin | Leflunomide may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. |
食物相互作用
- Take without regard to meals.