药品详细
Diclofenac (双氯芬酸 )
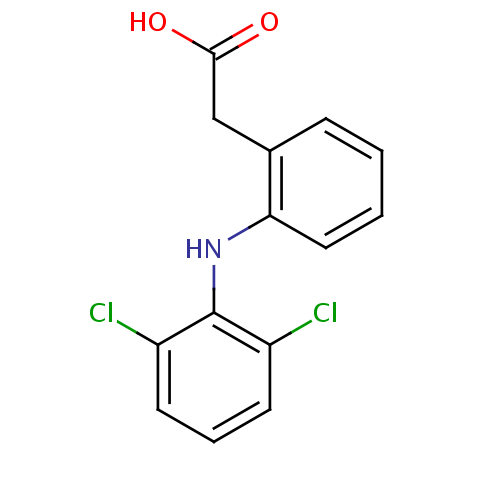
化学结构式图
中文名
双氯芬酸
英文名
Diclofenac
分子式
Not Available
化学名
2-{2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
分子量
Average: 296.149
Monoisotopic: 295.016684015
Monoisotopic: 295.016684015
CAS号
15307-86-5
ATC分类
M01A 未知;M02A 未知;S01B 抗炎药;D11A 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
商品名
Allvoran;Apo-Diclo;Assaren;Benfofen;Cataflam;Delphimix;Dichlofenac;Dichronic;Diclo-Phlogont;Diclo-Puren;Diclobenin;Diclord;Dicloreum;Dolobasan;Duravolten;Dyloject;Ecofenac;Effekton;Kriplex;Neriodin;Novapirina;Novo-Difenac;Novo-Difenac SR;Nu-Diclo;Pennsaid;Primofenac;Prophenatin;ProSorb-D;Rhumalgan;Solaraze;Solaraze T;Tsudohmin;Valetan;Voldal;Voltaren;Voltaren Ophtha;Voltaren Ophthalmic;Voltaren Rapide;Voltaren SR;Voltaren-XR;Voltarol;Xenid;
同义名
Diclofenac Acid;Diclofenac Potassium;Diclofenac Sodium;ISV-205;
基本介绍
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) with antipyretic and analgesic actions. It is primarily available as the sodium salt. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Actavis elizabeth llc
- Akorn inc
- Alcon inc
- Alphapharm party ltd
- Apotex inc
- Apotex inc richmond hill
- Bausch and lomb inc
- Biovail laboratories inc
- Carlsbad technology inc
- Dexcel ltd
- Falcon pharmaceuticals ltd
- Institut biochemique sa
- Mallinckrodt inc
- Mutual pharmaceutical co inc
- Mylan pharmaceuticals inc
- Nautilus neurosciences inc
- Nexus pharmaceuticals inc
- Nostrum laboratories inc
- Novartis consumer health inc
- Novartis pharmaceuticals corp
- Nycomed us inc
- Pliva inc
- Roxane laboratories inc
- Sandoz inc
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa
- Teva pharmaceuticals usa inc
- Unique pharmaceutical laboratories
- Watson laboratories inc
- Xanodyne pharmaceutics inc
封装厂家
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
| Form | Route | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Solution | Ophthalmic | |
| Solution | Topical | |
| Suppository | Rectal | |
| Tablet | Oral | |
| Tablet, coated | Oral | |
| Tablet, extended release | Oral |
规格
| Unit description | Cost | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltaren Ophtha 0.1 % Solution | 2.73 USD | ml |
| Voltaren 100 mg Suppository | 1.88 USD | suppository |
| Voltaren Sr 100 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 1.86 USD | tablet |
| Voltaren 50 mg Suppository | 1.4 USD | suppository |
| Voltaren Sr 75 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 1.31 USD | tablet |
| Voltaren 50 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.93 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac 100 mg Suppository | 0.88 USD | suppository |
| Sandoz Diclofenac 100 mg Suppository | 0.88 USD | suppository |
| Novo-Difenac Sr 100 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.8 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac-Sr 100 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.8 USD | tablet |
| Sandoz Diclofenac Sr 100 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.8 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac 50 mg Suppository | 0.65 USD | suppository |
| Sandoz Diclofenac 50 mg Suppository | 0.65 USD | suppository |
| Novo-Difenac Sr 75 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.6 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac-Sr 75 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.6 USD | tablet |
| Sandoz Diclofenac Sr 75 mg Sustained-Release Tablet | 0.6 USD | tablet |
| Apo-Diclo 50 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.4 USD | tablet |
| Novo-Difenac 50 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.4 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac 50 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.4 USD | tablet |
| Sandoz Diclofenac 50 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.4 USD | tablet |
| Apo-Diclo 25 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.2 USD | tablet |
| Novo-Difenac 25 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.2 USD | tablet |
| Nu-Diclo 25 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.2 USD | tablet |
| Pms-Diclofenac 25 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.2 USD | tablet |
| Sandoz Diclofenac 25 mg Enteric-Coated Tablet | 0.2 USD | tablet |
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC 消炎抗风湿;
药理
| Indication | For the acute and chronic treatment of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Diclofenac is an acetic acid nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Diclofenac is used to treat pain, dysmenorrhea, ocular inflammation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and actinic keratosis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | The antiinflammatory effects of diclofenac are believed to be due to inhibition of both leukocyte migration and the enzyme cylooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2), leading to the peripheral inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. As prostaglandins sensitize pain receptors, inhibition of their synthesis is responsible for the analgesic effects of diclofenac. Antipyretic effects may be due to action on the hypothalamus, resulting in peripheral dilation, increased cutaneous blood flow, and subsequent heat dissipation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption | Completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume of distribution |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein binding | More than 99% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism |
Hepatic
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of elimination | Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Half life | 2 hours | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clearance |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity | Symptoms of overdose include loss of consciousness, increased intracranial pressure, and aspiration pneumonitis. LD50=390mg/kg (orally in mice) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways |
|
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 283-285oC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Alendronate | Increased risk of gastric toxicity |
| Anisindione | The NSAID, diclofenac, may increase the anticoagulant effect of anisindione. |
| Cyclosporine | Monitor for nephrotoxicity |
| Dicumarol | The NSAID, diclofenac, may increase the anticoagulant effect of dicumarol. |
| Ginkgo biloba | Additive anticoagulant/antiplatelet effects may increase bleed risk. Concomitant therapy should be avoided. |
| Lithium | The NSAID, diclofenac, may decrease the renal excretion of lithium. Increased risk of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | The NSAID, diclofenac, may decrease the renal excretion of methotrexate. Increased risk of methotrexate toxicity. |
| Rifampin | Rifampin, a CYP2C9 inducer, may increase the metabolism of diclofenac. |
| Tacrine | The metabolism of Tacrine, a CYP1A2 substrate, may be reduced by Diclofenac, a CYP1A2 inhibitors. Monitor the efficacy and toxicity of Tacrine if Diclofenac is initiated, discontinued or if the dose is changed. |
| Telmisartan | Concomitant use of Telmisartan and Diclofenac may increase the risk of acute renal failure and hyperkalemia. Monitor renal function at the beginning and during treatment. |
| Timolol | The NSAID, Diclofenac, may antagonize the antihypertensive effect of Timolol. |
| Tizanidine | Diclofenac may decrease the metabolism and clearance of Tizanidine. Consider alternate therapy or use caution during co-administration. |
| Trandolapril | The NSAID, Diclofenac, may reduce the antihypertensive effect of Trandolapril. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in Trandolapril efficacy if Diclofenac is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Treprostinil | The prostacyclin analogue, Treprostinil, may increase the risk of bleeding when combined with the NSAID, Diclofenac. Monitor for increased bleeding during concomitant thearpy. |
| Voriconazole | Voriconazole, a strong CYP2C9 inhibitor, may increase the serum concentration of diclofenac by decreasing its metabolism. Renal impairment may increase the risk of diclofenac adverse effects. Monitor for changes in therapeutic and adverse effects of diclofenac if voriconazole is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Warfarin | The antiplatelet effects of oral diclofenac may increase the bleed risk associated with warfarin. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding during concomitant therapy. |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Take with food to reduce irritation.
