药品详细
Acetylcysteine(乙酰半胱氨酸)
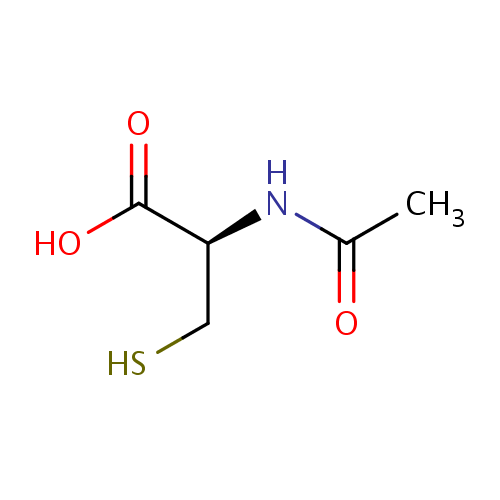
化学结构式图
中文名
乙酰半胱氨酸
英文名
Acetylcysteine
分子式
C5H9NO3S
化学名
(2R)-2-acetamido-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
分子量
Average: 163.195
Monoisotopic: 163.030313849
Monoisotopic: 163.030313849
CAS号
616-91-1
ATC分类
R05C 未知;S01X 其他眼科用药;V03A 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
同义名
基本介绍
Acetylcysteine is the N-acetyl derivative of cysteine. It is used as a mucolytic agent to reduce the viscosity of mucous secretions. It has also been shown to have antiviral effects in patients with HIV due to inhibition of viral stimulation by reactive oxygen intermediates. [PubChem]
生产厂家
- Apothecon inc div bristol myers squibb
- Bedford laboratories div ben venue laboratories inc
- Cumberland pharmaceuticals inc
- Dey lp
- Hospira inc
- Luitpold pharmaceuticals inc
- Roxane laboratories inc
封装厂家
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
药理
| Indication | Acetylcysteine is used mainly as a mucolytic and in the management of paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose. |
| Pharmacodynamics | Acetylcysteine has been shown to reduce the extent of liver injury following acetaminophen overdose. It is most effective when given early, with benefit seen principally in patients treated within 8-10 hours of the overdose. Acetylcysteine likely protects the liver by maintaining or restoring the glutathione levels, or by acting as an alternate substrate for conjugation with, and thus detoxification of, the reactive metabolite. |
| Mechanism of action | Acetylcysteine may protect against acetaminophen overdose-induced hepatotoxicity by maintaining or restoring hepatic concentrations of glutathione. It does this by producing the glutathione precursor cysteine. Glutathione is required to inactivate an intermediate metabolite (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine) of acetaminophen that is thought to be hepatotoxic. In acetaminophen overdose, excessive quantities of this metabolite are formed because the primary metabolic (glucuronide and sulfate conjugation) pathways become saturated. Acetylcysteine may act by reducing the metabolite to the parent compound and/or by providing sulfhydryl for conjugation of the metabolite. Experimental evidence also suggests that a sulfhydryl-containing compound such as acetylcysteine may also directly inactivate the metabolite. When inhaled, cetylcysteine exerts its mucolytic action through its free sulfhydryl group, which opens the disulfide bonds and lowers mucus viscosity. This action increases with increasing pH and is most significant at pH 7 to 9. The mucolytic action of acetylcysteine is not affected by the presence of DNA. Acetylcysteine is also an antioxidant and reduces oxidative stress. |
| Absorption | Bioavailability is 6–10% following oral administration and less than 3% following topical administration. |
| Volume of distribution | Not Available |
| Protein binding | 83% |
| Metabolism |
Hepatic. Deacetylated by the liver to cysteine and subsequently metabolized.
|
| Route of elimination | Not Available |
| Half life | 5.6 hours (adults), 11 hours (neonates) |
| Clearance | Not Available |
| Toxicity | Single intravenous doses of acetylcysteine at 1000 mg/kg in mice, 2445 mg/kg in rats, 1500 mg/kg in guinea pigs, 1200 mg/kg in rabbits and 500 mg/kg in dogs were lethal. Symptoms of acute toxicity were ataxia, hypoactivity, labored respiration, cyanosis, loss of righting reflex and convulsions. |
| Affected organisms |
|
| Pathways | Not Available |
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
食物相互作用
Not Available