药品详细
Bimatoprost(比马前列素)
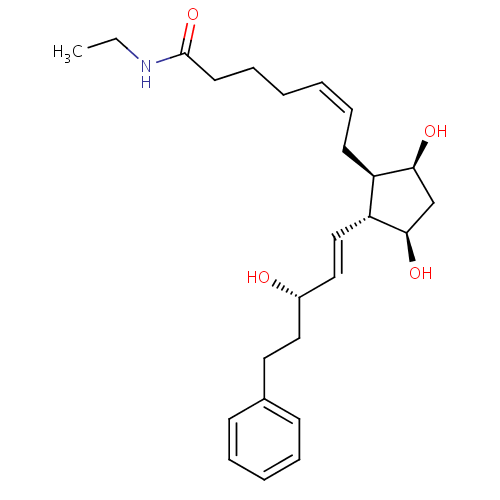
化学结构式图
中文名
比马前列素
英文名
Bimatoprost
分子式
C25H37NO4
化学名
(5Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-2-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-phenylpent-1-en-1-yl]cyclopentyl]-N-ethylhept-5-enamide
分子量
Average: 415.5656
Monoisotopic: 415.272258677
Monoisotopic: 415.272258677
CAS号
155206-00-1
ATC分类
S01E 抗青光眼制剂及缩瞳药
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
同义名
基本介绍
Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution is a topical medication used for controlling the progression of glaucoma or ocular hypertension, by reducing intraocular pressure. It is a prostaglandin analogue that works by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes. It binds to the prostanoid FP receptor.
生产厂家
- Allergan inc
封装厂家
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference |
|
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
药理
| Indication | For the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension who are intolerant of other intraocular pressure lowering medications or insufficiently responsive (failed to achieve target IOP determined after multiple measurements over time) to another intraocular pressure lowering medication. |
| Pharmacodynamics | Bimatoprost is a prostamide, a synthetic structural analog of prostaglandin with ocular hypotensive activity, that is chemically related to prostamide F. It selectively mimics the effects of naturally occurring substances, prostamides. Bimatoprost lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) in humans. Elevated IOP presents a major risk factor for glaucomatous field loss. The higher the level of IOP, the greater the likelihood of optic nerve damage and visual field loss. |
| Mechanism of action | Bimatoprost is believed to lower intraocular pressure (IOP) in humans by increasing outflow of aqueous humor through both the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral routes. Bimatoprost reduces the pressure in the eye by mimicking the action of a naturally-occuring prostaglandin. Prostaglandins are a group of chemicals found in many places in the body. In the eye, they increase the drainage of the aqueous humour out of the eyeball. Bimatoprost is a synthetic compound related to one of the natural prostaglandins, and works by increasing the drainage of aqueous humour out of the eyeball. Bimatoprost may also lower the rate of aqueous formation in the eye. Both these effects decrease the pressure within the eye. |
| Absorption | Systemically absorbed when administered to the eye. |
| Volume of distribution |
|
| Protein binding | Approximately 88% of bimatoprost is bound in human plasma. |
| Metabolism |
Bimatoprost undergoes oxidation, N-deethylation and glucuronidation to form a variety of metabolites.
|
| Route of elimination | Up to 67% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine while 25% of the dose was recovered in the feces. |
| Half life | Elimination half-life is approximately 45 minutes. |
| Clearance |
|
| Toxicity | In oral (by gavage) mouse and rat studies, doses up to 100 mg/kg/day did not produce any toxicity. This dose expressed as mg/m2 is at least 70 times higher than the accidental dose of one bottle of bimatoprost for a 10 kg child. |
| Affected organisms |
|
| Pathways | Not Available |
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Latanoprost | The concomitant use of bimatoprost and latanoprost may result in increased intraocular pressure. Consider avoiding this combination of therapy. Monitor for paradoxical increases in intraocular pressure during concomitant use. |
食物相互作用
Not Available