药品详细
Theophylline(茶碱)
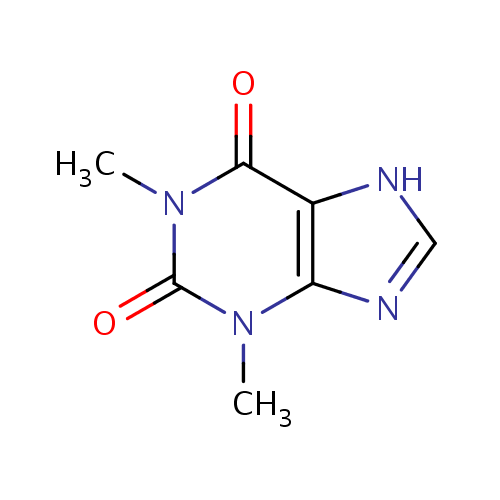
化学结构式图
中文名
茶碱
英文名
Theophylline
分子式
C7H8N4O2
化学名
1,3-dimethyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione
分子量
Average: 180.164
Monoisotopic: 180.06472552
Monoisotopic: 180.06472552
CAS号
58-55-9
ATC分类
R03D 未知;R03D 未知
药物类型
small molecule
阶段
approved
商品名
同义名
基本介绍
A methylxanthine derivative from tea with diuretic, smooth muscle relaxant, bronchial dilation, cardiac and central nervous system stimulant activities. Mechanistically, theophylline acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, adenosine receptor blocker, and histone deacetylase activator. Theophylline is marketed under several brand names such as Uniphyl and Theochron, and it is indicated mainly for asthma, bronchospasm, and COPD.
生产厂家
- 3m pharmaceuticals inc
- Able laboratories inc
- Alpharma us pharmaceuticals division
- B braun medical inc
- Baxter healthcare corp
- Caraco pharmaceutical laboratories ltd
- Cenci powder products inc
- Central pharmaceuticals inc
- Dm graham laboratories inc
- Ferndale laboratories inc
- Fisons corp
- Fleming and co pharmaceuticals inc
- Forest laboratories inc
- Glenmark generics ltd
- Graceway pharmaceuticals llc
- Halsey drug co inc
- Hospira inc
- Hr cenci laboratories inc
- Inwood laboratories inc sub forest laboratories inc
- Kv pharmaceutical co
- L perrigo co
- Lannett co inc
- Monarch pharmaceuticals inc
- Nostrum pharmaceuticals inc
- Novartis consumer health inc
- Ortho mcneil pharmaceutical inc
- Panray corp sub ormont drug and chemical co inc
- Pharmaceutical assoc inc div beach products
- Pharmaceutical research assoc inc
- Pliva inc
- Precision dose inc
- Purdue pharmaceutical products lp
- Roerig div pfizer inc
- Roxane laboratories inc
- Rp scherer north america
- Rp scherer north america div rp scherer corp
- Sandoz inc
- Sanofi aventis us llc
- Schering corp
- Schering corp sub schering plough corp
- Schwarz pharma inc
- Taro pharmaceuticals usa inc
- Ucb inc
- Warner chilcott co llc
- Whitby pharmaceuticals inc
- Wockhardt eu operations (swiss) ag
封装厂家
- Actavis Group
- Amend
- American Regent
- Amerisource Health Services Corp.
- Amneal Pharmaceuticals
- Apotheca Inc.
- Arcola Laboratories
- A-S Medication Solutions LLC
- Atlantic Biologicals Corporation
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- BASF Corp.
- Baxter International Inc.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.
- C.O. Truxton Inc.
- Cardinal Health
- Caremark LLC
- Central Texas Community Health Centers
- Comprehensive Consultant Services Inc.
- Direct Dispensing Inc.
- Dispensing Solutions
- Diversified Healthcare Services Inc.
- Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- Equipharm Inc.
- Forest Laboratories Inc.
- Forest Pharmaceuticals
- Glenmark Generics Ltd.
- H and H Laboratories
- Heartland Repack Services LLC
- Hospira Inc.
- Inwood Labs
- Inyx Usa Ltd.
- Kaiser Foundation Hospital
- Luitpold Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Major Pharmaceuticals
- Marlop Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Mckesson Corp.
- Mundipharma GmbH
- Murfreesboro Pharmaceutical Nursing Supply
- Nostrum Laboratories Inc.
- Nucare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- P F Laboratories Inc.
- PCA LLC
- PD-Rx Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Pharmaceutical Packaging Center
- Pharmaceutical Utilization Management Program VA Inc.
- Pharmedix
- Physicians Total Care Inc.
- Pliva Inc.
- Prepackage Specialists
- Prepak Systems Inc.
- Purdue Pharma LP
- Qualitest
- Remedy Repack
- Rite Aid Corp.
- Roxane Labs
- Roxmar Laboratories
- Sandhills Packaging Inc.
- Sandoz
- Sanofi-Aventis Inc.
- Southwood Pharmaceuticals
- Talbert Medical Management Corp.
- Taro Pharmaceuticals USA
- Tya Pharmaceuticals
- UCB Pharma
- United Research Laboratories Inc.
- Vangard Labs Inc.
- Warrick Pharmaceuticals Corp.
- Wockhardt Ltd.
参考
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
| General Reference | Not Available |
剂型
规格
化合物类型
| Type | small molecule |
| Classes |
|
| Substructures |
|
适应症
药理
| Indication | For the treatment of the symptoms and reversible airflow obstruction associated with chronic asthma and other chronic lung diseases, such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacodynamics | Theophylline, an xanthine derivative chemically similar to caffeine and theobromine, is used to treat asthma and bronchospasm. Theophylline has two distinct actions in the airways of patients with reversible (asthmatic) obstruction; smooth muscle relaxation (i.e., bronchodilation) and suppression of the response of the airways to stimuli (i.e., non-bronchodilator prophylactic effects). | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | Theophylline relaxes the smooth muscle of the bronchial airways and pulmonary blood vessels and reduces airway responsiveness to histamine, methacholine, adenosine, and allergen. Theophylline competitively inhibits type III and type IV phosphodiesterase (PDE), the enzyme responsible for breaking down cyclic AMP in smooth muscle cells, possibly resulting in bronchodilation. Theophylline also binds to the adenosine A2B receptor and blocks adenosine mediated bronchoconstriction. In inflammatory states, theophylline activates histone deacetylase to prevent transcription of inflammatory genes that require the acetylation of histones for transcription to begin. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption | Theophylline is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration in solution or immediate-release solid oral dosage form. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume of distribution |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein binding | 40%, primarily to albumin. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism |
Hepatic. Biotransformation takes place through demethylation to 1-methylxanthine and 3-methylxanthine and hydroxylation to 1,3-dimethyluric acid. 1-methylxanthine is further hydroxylated, by xanthine oxidase, to 1-methyluric acid. About 6% of a theophylline dose is N-methylated to caffeine. Caffeine and 3-methylxanthine are the only theophylline metabolites with pharmacologic activity.
Important The metabolism module of DrugBank is currently in beta. Questions or suggestions? Please contact us.
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of elimination | Theophylline does not undergo any appreciable pre-systemic elimination, distributes freely into fat-free tissues and is extensively metabolized in the liver. Renal excretion of unchanged theophylline in neonates amounts to about 50% of the dose, compared to about 10% in children older than three months and in adults. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Half life | 8 hours | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Clearance |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity | Symptoms of overdose include seizures, arrhythmias, and GI effects. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected organisms |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
理化性质
| Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
药物相互作用
| Drug | Interaction |
|---|---|
| Acyclovir | Acyclovir may increase the effect and toxicity of theophylline. |
| Adenosine | Theophylline may decrease the effect of adenosine. |
| Amobarbital | The barbiturate, amobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Aprobarbital | The barbiturate, aprobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Atracurium | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Bromazepam | Theophylline may decrease the therapeutic effect of bromazepam. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic effects of bromazepam if theophylline is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Butabarbital | The barbiturate, butabarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Butalbital | The barbiturate, butalbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Butethal | The barbiturate, butethal, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Carbamazepine | Carbamazepine may decrease the serum concentration of theophylline. Theophylline may decrease the serum concentration of carbamazepine. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic effect of both agents if concomitant therapy is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Carteolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Cimetidine | Cimetidine may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Ciprofloxacin | Ciprofloxacin may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Clarithromycin | Clarithromycin may increase the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline. |
| Dihydroquinidine barbiturate | The barbiturate, dihydroquinidine barbiturate, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Disulfiram | Disulfiram may increase the effect and toxicity of theophylline. |
| Doxacurium chloride | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Enoxacin | Enoxacin may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Erythromycin | The macrolide, erythromycin, may increase the effect and toxicity of theophylline. |
| Ethinyl Estradiol | The contraceptive increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Ethotoin | Decreased effect of both products |
| Febuxostat | Coadministration of febuxostat with xanthine oxidase substrate drugs (azathioprine, mercaptopurine or theophylline) could increase plasma concentrations of these drugs, since these drugs are metabolized by xanthine oxidase, resulting in severe toxicity; hence their concomitant use is contraindicated. Since febuxostat does not inhibit or induce cytochrome P450 enzymes it lacks significant drug interactions with other drugs metabolized of these enzymes. |
| Fluvoxamine | Fluvoxamine may increase the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline. |
| Fosphenytoin | Decreased effect of both products |
| Grepafloxacin | Grepafloxacin may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Halothane | Increased risk of cardiac arrhythmia |
| Heptabarbital | The barbiturate, heptabarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Hexobarbital | The barbiturate, hexobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Interferon Alfa-2a, Recombinant | Interferon increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Interferon Alfa-2b, Recombinant | Interferon increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Interferon alfa-n1 | Interferon increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Isoniazid | Isoniazid may increase the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline. |
| Josamycin | The macrolide, josamycin, may increase the effect and toxicity of theophylline. |
| Lithium | Theophylline decreases serum levels of lithium |
| Mephenytoin | Decreased effect of both products |
| Mestranol | The contraceptive increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Methohexital | The barbiturate, methohexital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Methylphenobarbital | The barbiturate, methylphenobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Metocurine | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Mexiletine | Mexiletine increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Mivacurium | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Nadolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Norfloxacin | Norfloxacin may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Pancuronium | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Pefloxacin | Pefloxacin may increase the effect of theophylline. |
| Peginterferon alfa-2a | Interferon increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Peginterferon alfa-2b | Interferon increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Penbutolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Pentobarbital | The barbiturate, pentobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Pentoxifylline | Pentoxifylline increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Phenobarbital | The barbiturate, phenobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Phenytoin | Decreased effect of both products |
| Pindolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Primidone | The barbiturate, primidone, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Propafenone | Propafenone increases the effect of theophylline |
| Propranolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Quinidine barbiturate | The barbiturate, quinidine barbiturate, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Regadenoson | Non-specific adenosine receptor antagonist may interfere with the vasodilation activity of regadenoson. Avoid methylxanthines for at least 12 hours before administration of regadenoson. |
| Rifampin | Rifampin decreases the effect of theophylline |
| Ritonavir | Ritonavir decreases the effect of theophylline |
| Rofecoxib | Rofecoxib increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Secobarbital | The barbiturate, secobarbital, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Sotalol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| St. John's Wort | St. John's Wort decreases the effect of theophylline |
| Tacrine | Tacrine may reduce the elimination rate of Theophylline. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and toxic effects of theophylline if Tacrine is initiated, discontinued or if the dose is changed. |
| Talbutal | The barbiturate, talbutal, decreases the effect of theophylline. |
| Telithromycin | Telithromycin may reduce clearance of Theophylline. Consider alternate therapy or monitor for changes in the therapeutic/adverse effects of Theophylline if Telithromycin is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Temazepam | Theophylline may decrease the efficacy of Temazepam. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic effect of Temazepam if Theophylline is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Terbinafine | Terbinafine increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Thiabendazole | The strong CYP1A2 inhibitor, Thiabendazole, may increase the effects and toxicity of Theophylline by decreasing Theophylline metabolism and clearance. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of Theophylline if Thiabendazole is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Ticlopidine | Ticlopidine increases the effect and toxicity of theophylline |
| Timolol | Antagonism of action and increased effect of theophylline |
| Tipranavir | Tipranavir, co-administered with Ritonavir, may decrease the concentration of Theophylline. |
| Troleandomycin | The macrolide, troleandomycin, may increase the effect and toxicity of theophylline. |
| Tubocurarine | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Vecuronium | Theophylline decreases the effect of the muscle relaxant |
| Verapamil | Verapamil increases the effect of theophylline |
| Voriconazole | Voriconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, may increase the serum concentration of theophylline by decreasing its metabolism. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline if voriconazole is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. |
| Zafirlukast | Zafirlukast serum concentrations may be decreased by Theophylline. |
| Zileuton | Zileuton may increase the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline by increasing its serum concentration. Monitor for changes in the therapeutic and adverse effects of theophylline if zileuton is initiated, discontinued or dose changed. Dose alterations should be considered. |
食物相互作用
- Avoid alcohol.
- Avoid excessive quantities of coffee or tea (Caffeine).
- Take with food.